Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that is commonly performed in cardiology to treat coronary artery disease (CAD). The procedure involves using a balloon catheter to dilate narrowed or blocked coronary arteries, thereby restoring blood flow to the heart muscle. Angioplasty is often performed as part of a larger treatment plan for CAD, which may also include lifestyle changes, medication, or coronary artery bypass surgery. In this article, we will explore the different types of angioplasty, the indications for the procedure, and its associated risks and benefits.
Types of Angioplasty: There are several different types of angioplasty, each of which is used to treat different types of coronary artery disease. The most common types of angioplasty include:
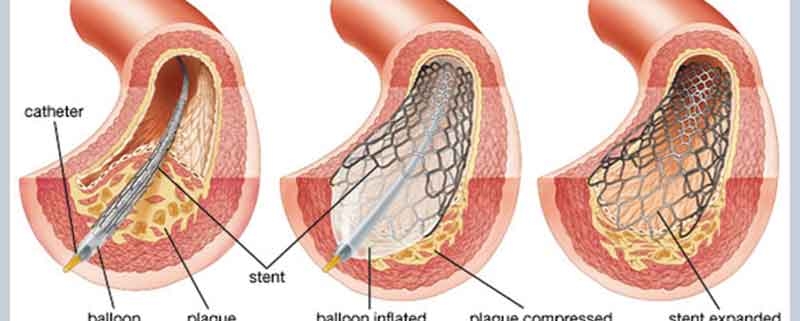
- Balloon angioplasty: Balloon angioplasty is the most common type of angioplasty. During this procedure, a small balloon is inserted into the blocked or narrowed coronary artery and inflated to widen the artery and restore blood flow.
- Drug-eluting stent: A drug-eluting stent is a small mesh tube that is inserted into the blocked or narrowed coronary artery. The stent is coated with a medication that is slowly released over time to prevent the artery from narrowing again.
- Coronary atherectomy: Coronary atherectomy is a procedure that involves using a small device to remove plaque from the walls of the coronary arteries. This procedure is often used in cases where the plaque is too hard or calcified to be treated with balloon angioplasty.
Indications for Angioplasty: Angioplasty is typically recommended for patients with significant blockages or narrowing of the coronary arteries. The procedure may be indicated in cases where the patient is experiencing symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or fatigue, which are often caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
Angioplasty may also be recommended for patients who have had a heart attack, as restoring blood flow to the affected area of the heart can help to prevent further damage and improve long-term outcomes. In some cases, angioplasty may also be recommended as a preventive measure for patients who are at high risk of developing CAD, such as those with a family history of the condition or those with multiple risk factors, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes.
Risks and Benefits of Angioplasty: Like any medical procedure, angioplasty carries some risks, including bleeding, infection, and damage to the blood vessels or surrounding tissues. In rare cases, patients may experience more serious complications, such as heart attack, stroke, or kidney damage.
However, for most patients, the benefits of angioplasty far outweigh the risks. By restoring blood flow to the heart muscle, angioplasty can help to relieve symptoms, improve quality of life, and reduce the risk of heart attack and other complications. For many patients, angioplasty is an effective and relatively low-risk treatment option for coronary artery disease.
Conclusion: In conclusion, angioplasty is a common and effective treatment option for patients with coronary artery disease. The procedure is minimally invasive and can be performed on an outpatient basis, with most patients able to return to normal activities within a few days. While angioplasty carries some risks, for most patients, the benefits of the procedure far outweigh the potential complications. If you are experiencing symptoms of CAD or have been diagnosed with the condition, talk to your doctor about whether angioplasty may be a good treatment option for you.