Clinical and Critical Cardiology: Understanding the Importance of Heart Health
Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 17.9 million people died from cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) in 2019, accounting for 32% of all global deaths. In the United States alone, heart disease is responsible for one in four deaths, making it the leading cause of death for both men and women.
Clinical and critical cardiology are two essential fields of medicine that deal with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of heart diseases. These two areas of cardiology are crucial in ensuring the optimal care of patients with heart conditions.
What is Clinical Cardiology?
Clinical cardiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of heart diseases. Clinical cardiologists specialize in the management of patients with various heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease, and arrhythmias.
A clinical cardiologist typically evaluates patients who have symptoms of heart disease, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, or fatigue. The cardiologist conducts a comprehensive evaluation, including a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, stress test, or cardiac catheterization.
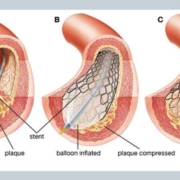
Based on the evaluation, the cardiologist provides a diagnosis and recommends an appropriate treatment plan, which may include medications, lifestyle modifications, or procedures such as angioplasty or heart surgery. The cardiologist also provides ongoing management and follow-up care to ensure that the patient’s heart condition is well-controlled and any potential complications are addressed promptly.
What is Critical Cardiology?
Critical cardiology is a specialized field of medicine that deals with the management of patients with acute or life-threatening heart conditions, such as acute myocardial infarction (heart attack), cardiogenic shock, or severe heart failure. Critical cardiologists work in intensive care units (ICUs) and provide round-the-clock care to patients who require close monitoring and advanced interventions.
Critical cardiologists are trained in advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) and are skilled in using various life-saving treatments and devices, such as mechanical ventilation, intra-aortic balloon pump, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). These treatments help support the patient’s heart function and vital organs until the underlying condition is treated.
In addition to providing advanced interventions, critical cardiologists work closely with other healthcare professionals, such as cardiac surgeons, nurses, respiratory therapists, and pharmacists, to ensure the optimal care of critically ill patients. The goal is to stabilize the patient’s condition, minimize complications, and improve the chances of a full recovery.
Why is Heart Health Important?
Heart health is essential for overall health and well-being. The heart is a vital organ that pumps blood and oxygen to all parts of the body, providing the necessary nutrients and energy for cells to function properly. When the heart is not functioning correctly, it can lead to various complications, such as heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, or even death.
Maintaining a healthy heart involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, and managing stress. In addition, it is crucial to managing any underlying medical conditions that may affect heart health, such as hypertension, high cholesterol, or diabetes.
Early detection and treatment of heart disease are critical in preventing complications and improving outcomes. Regular check-ups with a cardiologist can help identify any potential risk factors or early signs of heart disease, allowing for prompt intervention and treatment.
Conclusion
Clinical and critical cardiology are two critical areas of medicine that play a crucial role in ensuring the optimal care of patients with heart diseases.