Men and thyroid problems? It might sound uncommon, but an overactive thyroid, or hyperthyroidism, can significantly impact men’s health. This condition often whispers before it roars, with subtle signs that can be easily overlooked. This blog dives deep into hyperthyroidism in men, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and when to seek medical help.
Why Does My Thyroid Act Up?
The thyroid gland, located in your neck, is like a body’s master controller, regulating metabolism, energy, and hormones. When it goes rogue, producing too much thyroid hormone, hyperthyroidism disrupts everything.
Here’s what can trigger this imbalance in men:
- Autoimmune Attack: Graves’ disease, the most common culprit, tricks your immune system into attacking your thyroid, revving it up.
- Family Ties: A family history of thyroid issues raises your risk.
- Too Much or Too Little Iodine: Iodine is essential for thyroid function, but too much or too little can cause problems.
- Hidden Culprits: Certain medical conditions and even growths on the thyroid can affect hormone production.
Symptoms: Don’t Ignore the Whispers
Hyperthyroidism’s symptoms can be sneaky, mimicking other health concerns or stress. Here’s what to watch out for:
- Shrinking Waistline: Unexpected weight loss despite normal eating.
- Heat Wave: Feeling constantly hot and sweaty.
- Racing Heart: Rapid heartbeat and palpitations.
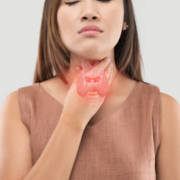
- Neck Lump: A swollen thyroid gland (goiter).
- Brain Fog: Difficulty concentrating or remembering things.
- Mood Swings: Feeling anxious, irritable, or on edge.
- Muscle Matters: Weakness and fatigue.
- Bedroom Blues: Reduced sex drive or erectile dysfunction.
- Bathroom Blues: Changes in bowel habits (diarrhea or constipation).
- Hair Loss: Thinning hair or hair loss.
- Dry Skin and Brittle Nails
- Sleepless Nights: Trouble falling asleep or staying asleep.
- Rarely: Breast enlargement (gynecomastia)
Getting a Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is key to managing hyperthyroidism. Doctors use a combination of approaches:
- Checking Your Neck: A physical exam to assess thyroid size and signs of increased metabolism.
- Blood Tests: Measuring hormone levels (TSH, T3, T4) to identify imbalances.
- Antibody Tests: Looking for specific antibodies in autoimmune cases (like Graves’ disease).
- Imaging Tests: Scans or ultrasounds to visualize the thyroid gland for abnormalities.
- Biopsy (if needed): A tissue sample examination to rule out cancer in case of nodules.
Treatment Options: Taking Back Control
The treatment plan depends on the severity, cause, and your overall health. Here are the main approaches:
- Medications: Antithyroid drugs can help regulate hormone production. Careful monitoring is crucial to avoid overcorrection or undercorrection.
- Radioactive Iodine (RAI) Therapy: A targeted approach using radioactive iodine to destroy overactive thyroid cells. This may lead to hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), requiring lifelong hormone replacement therapy.
- Surgery: In some cases, removing part or all of the thyroid gland might be necessary. This is a definitive solution but typically results in hypothyroidism, requiring hormone replacement therapy.
- Managing Symptoms: Medications or lifestyle changes can address specific symptoms like rapid heart rate, weight issues, fatigue, or sexual dysfunction.
Final Notes
Watch out for warning signs like unexplained weight changes, persistent mood swings, or irregular heartbeats. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial for managing hyperthyroidism effectively. If you notice any concerning symptoms or have a family history of thyroid problems, visit the doctor.
Ayushman Hospital & Health Services is a state-of-the-art facility with a team of highly trained experts dedicated to providing exceptional care for various health conditions, including thyroid problems. Schedule your appointment today!