Paediatric Cardiology: Understanding the Complexities of Children’s Heart Health
The heart is a crucial organ that pumps blood throughout the body, supplying vital oxygen and nutrients to all organs and tissues. Paediatric cardiology is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of heart disease in children from infancy to adolescence.
Children’s heart health is a complex subject that requires a deep understanding of both the anatomy and physiology of the heart, as well as the unique challenges that children face when it comes to heart health. In this blog post, we will explore some of the key aspects of paediatric cardiology, including common heart conditions in children, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options.
Common Heart Conditions in Children
Congenital Heart Defects
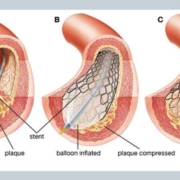
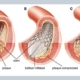
Congenital heart defects (CHD) are structural abnormalities that occur during the development of the heart and blood vessels in the womb. CHDs can range in severity from minor defects that may not require treatment, to life-threatening conditions that require immediate intervention.
Some of the most common types of CHDs include:
- Atrial septal defects (ASD): A hole in the wall between the two upper chambers of the heart.
- Ventricular septal defects (VSD): A hole in the wall between the two lower chambers of the heart.
- Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF): A combination of four heart defects that affect blood flow through the heart and lungs.
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA): Failure of a blood vessel that connects the aorta and pulmonary artery to close after birth.
- Coarctation of the aorta: Narrowing of the aorta that restricts blood flow to the lower body.
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are irregular heart rhythms that can affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. In children, arrhythmias can occur as a result of congenital heart defects, electrolyte imbalances, or underlying medical conditions.
Some common types of arrhythmias in children include:
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT): A rapid heart rate that originates in the upper chambers of the heart.
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT): A rapid heart rate that originates in the lower chambers of the heart.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW): A rare condition where an extra electrical pathway in the heart can cause rapid heart rates.
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a condition where the heart muscle becomes weak or stiff, making it difficult for the heart to pump blood effectively. In children, cardiomyopathy can be caused by genetic factors, viral infections, or other underlying medical conditions.
Some of the most common types of cardiomyopathy in children include:
- Dilated cardiomyopathy: The heart becomes enlarged and weakened, reducing its ability to pump blood effectively.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: The walls of the heart become thickened, making it harder for the heart to pump blood effectively.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy: The heart becomes stiff and unable to fill with blood properly.
Diagnostic Procedures in Paediatric Cardiology
Diagnosing heart conditions in children requires a thorough evaluation of the child’s medical history, physical examination, and a variety of diagnostic tests.
Some common diagnostic procedures in paediatric cardiology include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): A test that records the electrical activity of the heart and can help identify abnormal heart rhythms or other electrical abnormalities.
- Echocardiogram: A test that uses sound waves to create images of the heart and can help identify structural abnormalities or problems with the heart’s function.